NMC whistleblower case review finds nearly all reached ‘right outcome’
The right outcome was reached in 19 out of 20 historical fitness to practise (FtP) cases flagged by a Nursing and Midwifery Council (NMC) whistleblower in 2023, according to an independent review. The post NMC whistleblower case review finds nearly all reached ‘right outcome’ appeared first on Nursing Times.
New hospital design puts nurses at the ‘heart’ of care delivery
NHS England has placed nurses at the centre of its hospital-building programme, with a radical redesign of ward layouts and clinical spaces intended to transform working conditions and improve patient care. The post New hospital design puts nurses at the ‘heart’ of care delivery appeared first on Nursing Times.
Frontier Nursing University Introduces Office of Student Engagement, Access, and Success

Frontier remains committed to fostering an environment that values and supports all students and honors diverse backgrounds, perspectives, and experiences. VERSAILLES, Ky. – Frontier Nursing University (FNU) has established an Office of Student Engagement, Access, and Success. This strategic initiative places student success as the university’s central priority while ensuring comprehensive support from enrollment to […]
Lumbar Puncture Neuro NCLEX-Style Questions

Test your knowledge on lumbar puncture (LP), also called a spinal tap, procedures with this NCLEX-style quiz designed for nursing students and healthcare professionals. These questions cover key aspects of lumbar puncture care, including needle insertion sites, pre-procedure lab checks, medication precautions, patient positioning, interpretation of CSF opening pressure, and post-procedure interventions. Don’t forget to […]
Most Common Mispronounced Medical Terms Every Nursing Student Should Know
As nursing students, mastering medical terminology is essential not just for exams, but for clear communication in clinical settings. Yet, even the most experienced nurses can struggle with pronouncing certain terms (I know I definitely have). Let’s go over some of the most commonly mispronounced medical terms you’ll encounter in nursing school and practice. Sphygmomanometer […]
Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap) Nursing NCLEX Review
A lumbar puncture (LP), also called a spinal tap, is a common diagnostic procedure nursing students must understand for exams and clinical practice. During this procedure, a needle is inserted into the lower back (lumbar area), most often between the L3–L4 or L4–L5 vertebrae, to collect cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Because CSF surrounds and cushions the […]
New virtual dementia nurse clinic for underrepresented patients

A charity that provides specialist dementia nursing services has launched a new clinic service, accessible online or via phone, specifically to support Black, African and Caribbean communities. The post New virtual dementia nurse clinic for underrepresented patients appeared first on Nursing Times.
‘As health workers, we need to accept the flu vaccine – we may need it more than we think’
In her latest column, Linda Nazarko explores why influenza vaccination rates are dropping for both health professionals and the general public. The post ‘As health workers, we need to accept the flu vaccine – we may need it more than we think’ appeared first on Nursing Times.
Learning disability nursing workforce at risk of ‘imminent collapse’

A coalition of leading charities, campaigners and health organisations is warning of an imminent collapse in learning disability nursing that threatens the lives of thousands of people. The post Learning disability nursing workforce at risk of ‘imminent collapse’ appeared first on Nursing Times.
WWI Nurse Mary Nurney Finally Honored in Stamford, Makes History
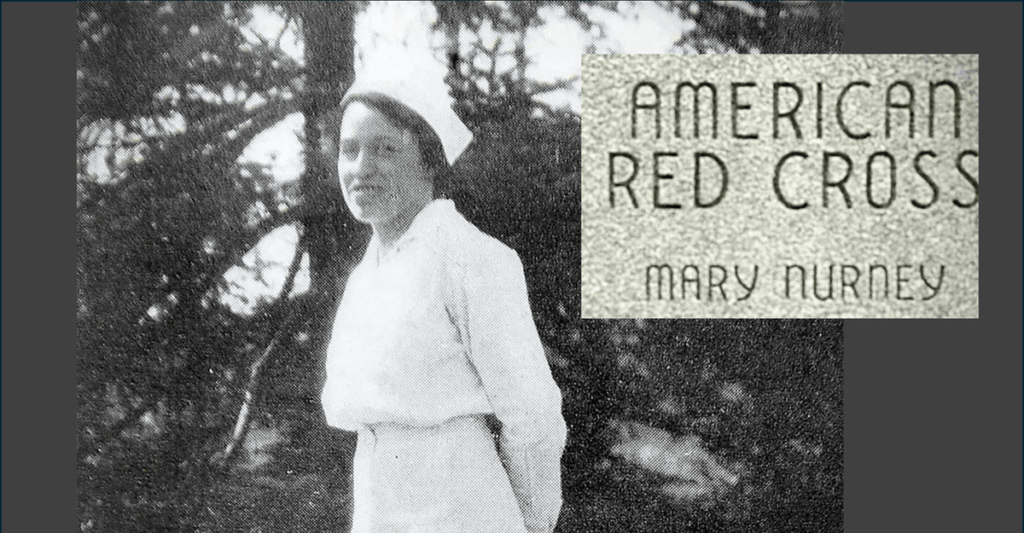
Image sources: CTInsider Mary Nurney, a Red Cross nurse in World War I, recently became the first woman honored on Stamford’s Memorial Wall, a recognition more than a century in…
